42 Pine Base Kitchen Cabinets With Drawers
Everything you Need to Know about Kitchen Cabinets
The cabinets alone can define your kitchen's style. However, aesthetics are not the only point to consider. Materials and construction methods are also very important factors. This buyer's guide is the perfect tool to help you make a wise choice.
3 types of cabinets, 3 construction methods
There are three main types of cabinets: base cabinets, wall cabinets and tall cabinets.
Base cabinets support the countertop. Their standard height is between 34 ½" and 36" and their standard depth varies between 24" and 30".
Wall cabinets hang on the wall and do not touch the floor. They can be 12", 15", 18", 30", 36" or 42" high. Their depth varies between 12" and 18". They are typically installed 18" above work surfaces and 54" above the floor.
Tall cabinets, for example pantries, are 84" to 94" high and come in standard depths of 12" to 18".
Within these 3 categories, cabinets are either stock (prefabricated), semi-custom or custom. When planning your kitchen renovations, determine how much you wish to spend on cabinets and how important durability and aesthetics are to you.
Types of cabinets

Stock cabinets
Sold pre-assembled in home improvement stores or kitchen centres, stock cabinets come in standard sizes.
Advantages
- Economical
- Shorter lead time
- Ideal for limited budgets
- Made in standard heights
Disadvantage
- Limited choice of configurations and finishes
Shop stop cabinets
Semi-custom cabinets
Semi-custom cabinets come in standard sizes. They are made to order and offer more personalized options.
Advantages
- More options than stock cabinets in terms of design, storage and style
- Wider choice of finishes and materials
- For mid-range budgets
Disadvantage
- Longer lead time for delivery than stock cabinets
Custom cabinets
Custom cabinets are made by kitchen designers according to the client's specifications.
Advantages
- Custom-made
- Fit the specifications of each kitchen
- Wider choice of materials, finishes and designs
- Generally made from higher-quality materials
Disadvantages
- Longest lead time
- Costly
Features of a Kitchen Cabinet
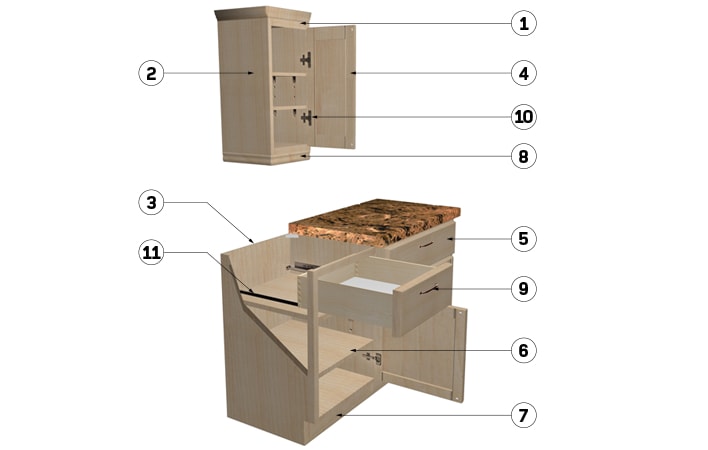
1. Face frame
Framed cabinets have a frame around the front of the cabinet box made of the same material as the drawers and doors. The frame stabilizes the box. Here, the hinges are visible and are attached directly to the frame.
Frameless (or European-style) cabinets have no frame around the cabinet box; the doors and drawers cover the box's edges. The side panels of the cabinet box are thicker to provide stability. The hinges are attached directly to the side panels, which offer greater storage space.
2. Sides
The sides of the cabinet are usually between ½" and ¾" thick. They are generally unfinished and are typically made of one of the following materials:
-
Particleboard: widely used in cabinet construction, but susceptible to bending and warping.
-
Medium-density fibreboard (MDF): less expensive than other materials but susceptible to water damage.
-
Plywood: considered an excellent choice for cabinet construction due to its strength and durability.
3. Back panel and bottom of cabinet
They support and ensure the rigidity of the whole cabinet. A back panel made of ½" plywood will prevent the cabinet from warping over time. However, a back panel of just ¼" thick is sufficient for a base cabinet, since it is not used to hold the cabinet to the wall.
4. Door
There are two types of cabinet doors – those made from a single piece of material, and those built from a frame and an inner panel. The latter comprises a wood frame with a central panel made either of wood or of MDF covered with the chosen finish.
Even though they have a more distinguished style, wooden doors may bend or warp over the years due to humidity. However, the surface will not peel and its colour will not fade.
Cabinets panels are grouped under 6 main categories:
5. Drawers
It is important to consider how they are constructed and their durability. First, it is important to know that the sides of solid wood drawers are 5/8" to ¾" thick. Drawers made from particleboard are only ½" thick and are more susceptible to warping, so they may not be the best long-term choice. For drawer bottoms, ¼" plywood is the best option.
Though wood drawers are the most popular option, some manufacturers make models with metal sides that are well suited to frameless cabinets.
Mortise and tenon joint
The mortise is a square hole made in one part and the tenon is the protruding peg on the other part that fits into the mortise. For an extra-sturdy structure, the tenon may pass all the way through the mortise, although the finished look may be less aesthetically pleasing.
Dovetail joint
Strong, high-quality joinery technique with superior resistance. Trapezoidal-shaped tenons are slotted into corresponding notches of the same shape on the adjoining part.
Dowelled joint
This technique uses round wood dowels (pegs) fitted into holes. Dowels can also be used to strengthen a mortise and tenon-typed joint.
Biscuit joint
These joints are made by slotting a piece of wood called a biscuit, into slots on the adjoining parts. The glue's humidity makes the biscuit swell and stay wedged in place, creating a strong bond. This quick and straightforward technique is increasingly used in cabinet joinery.
Tongue and groove joint
For this joint, a channel or groove is cut along the length of one piece and the projecting edge or tongue on the adjoining piece slots into it.
Frame and panel joint (rail and stile)
Similar to tongue and groove, frame and panel joinery consists in machining two parts into shapes (stiles and rails) that fit together. Since there is a large surface area for gluing, this type of joint is very strong.
6. Shelf
Shelves are available in fixed or pull-out versions, and are typically made of plywood, MDF or particleboard covered with a layer of another material such as wood veneer or laminate. Shelf thickness can vary from one manufacturer to another, or depending on the customer's requirements, but the standard measurements are ½", 5/8" and ¾".
The thicker the shelf, the less likely it is to buckle under weight. Nevertheless, if the shelf is going to be used to hold heavy items such as cans and preserves, it's important that the sides of the cabinet be thick enough to support the load.
7. Toe kick
The toe kick is a recessed area for feet, allowing you to stand closer to the countertop when preparing meals. It is generally 3" deep and 3 ½" high, though it can be made up to 10" high for wheelchair users.
Elements such as a central vacuum inlet or even additional drawers can be built into the toe kick. Decorative feet can also be added at the end of a line of cabinets to enhance the appearance.
8. Decorative mouldings and fillers
Decorative mouldings, as well as corbels, mosaics or columns enhance the look of cabinets, according to the desired style. This finishing touch can completely transform your kitchen.
9. Pulls, knobs and pendants
Drawer and cabinet pulls, knobs and pendants unify and enhance the overall look of the kitchen.
-
Pulls are fastened with two screws. They are available in a wide variety of styles to match all decors.
-
Knobs are attached with just one screw. They are mostly for decorative purposes.
-
Pendants are handles with a hinged back plate. They suit more opulent decors.
10. Hinges
Many types of cabinet hinges exist and your choice will largely be determined by the type of cabinet you have. Some hinges are fitted with soft-close mechanisms, which are practical for families with children.
-
Exposed hinges are partially or entirely visible when the cabinet doors are closed.
-
Concealed hinges cannot be seen when the doors are closed. Most of them are adjustable.
-
Mortise hinges require a mortise (notch) to be cut in the cabinet frame so that the wings of the hinge sit flush with the surface.
-
No-mortise hinges do not require a mortise to be cut in the cabinet frame; the wings are fastened directly to the cabinet surface.
-
Swing clear hinges allow the door to swing completely clear of the opening, providing unrestricted access to the inside of the cabinet.
11. Drawer slides (glides)
Some slides offer full extension, meaning that the drawer can be pulled out fully for easier access. Some slides are fitted with a handy soft-close mechanism, which allows the drawer to be closed smoothly and gently.
Drawer slides can support loads of up to 75-100 lbs. Choose slides that can support more weight if the drawer will be used to hold pots and pans or small appliances.
-
Ball-bearing slides are stable, simple and hard-wearing. The slides are mounted on each side of the drawer.
-
Undermount slides are fitted underneath the drawer, which increases the drawer's load-carrying capacity. They provide excellent support and stability.
-
Side-mount slides provide good support but offer a more limited access to the back of the drawer.
A wide selection of materials
Wood, wood veneer, melamine, laminate, lacquer, thermoplastic, stainless steel, glass... Whether it is designed in a rustic, modern or traditional style, each type of material has its own advantages.
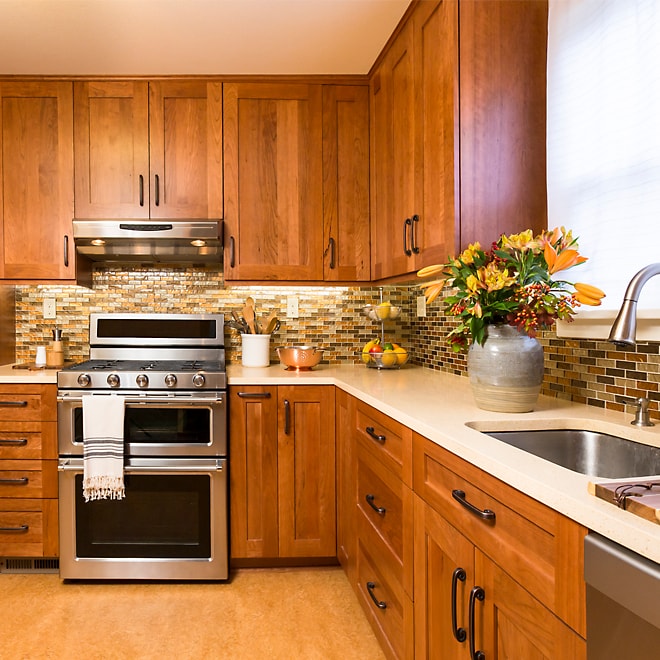

Solid wood
The most popular species are maple, birch, pine, mahogany, walnut, oak, cherry, hickory and exotic woods.
Advantages
- Timeless
- Sturdy
- Versatile
- Warm
- Suits all decors
- Maple, birch and oak are the most popular choices due to their durability
- Exotic species are becoming increasingly popular due to their rich, warm tones
Disadvantages
- Sensitive to humidity
- Relatively expensive
- Pine is less expensive than other wood species but more fragile and more susceptible to bumps and scratches
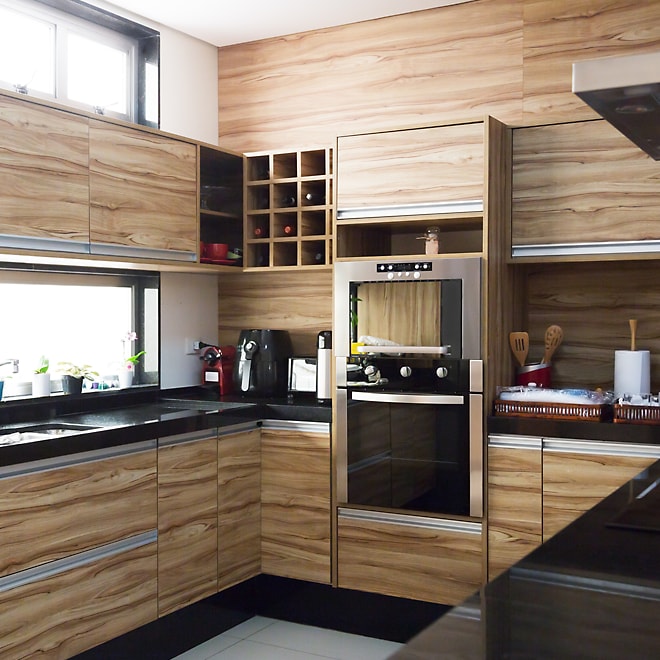

Wood veneer
Made from a thin layer of wood adhered to plywood.
Advantages
- Less costly than solid wood
- Better resistance to humidity
Disadvantage
- Less resistant to scratches than solid wood
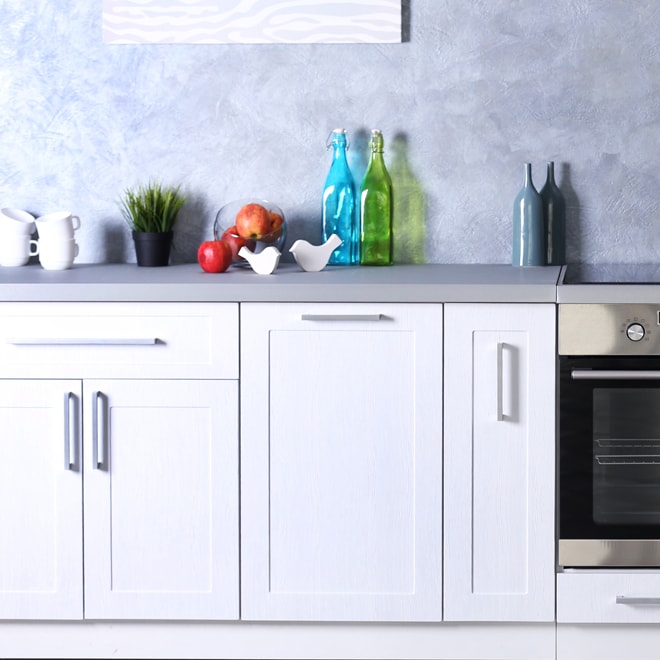

Melamine
Decorative paper impregnated with resin, glued to pressed wood.
Advantages
- Wide range of colours and patterns
- Inexpensive
Disadvantages
- May chip under impact
- Hard to repair if damaged
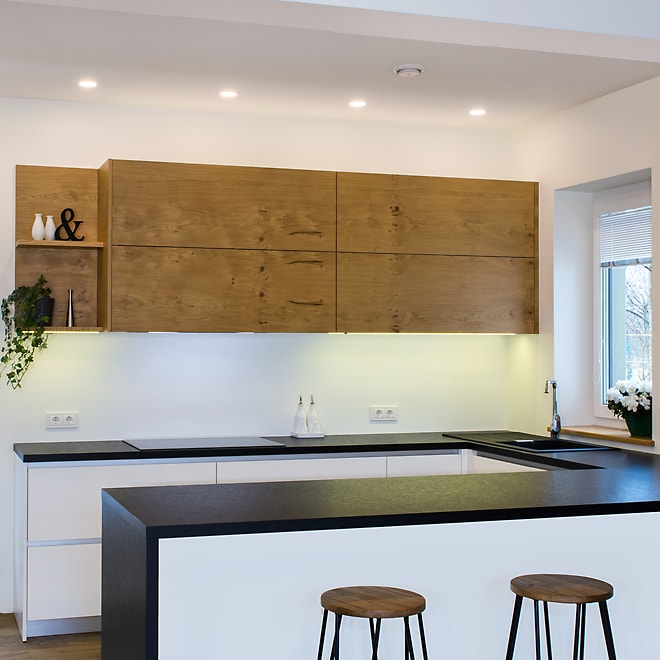

Laminate
Made from thin sheets of resin-impregnated paper, heat-sealed together.
Advantages
- Much more durable than melamine
- Wide range of colours and textures
Disadvantage
- More expensive than melamine
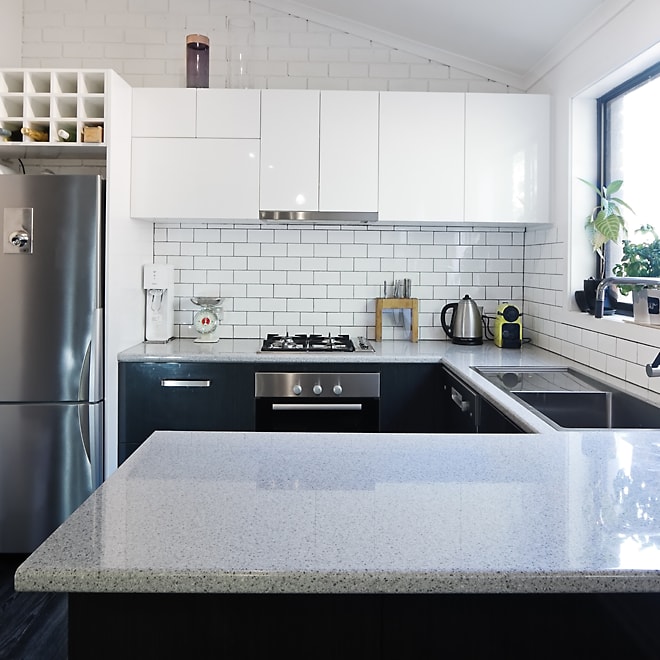

Enamelled or lacquer board
Fibreboard coated with lacquer.
Advantages
- Allows sleek or modern sculpted designs
- Wide choice of finishes
Disadvantages
- Relatively costly
- Difficult to keep clean
- Glossy finish can change quickly
- White lacquer may turn yellow over time
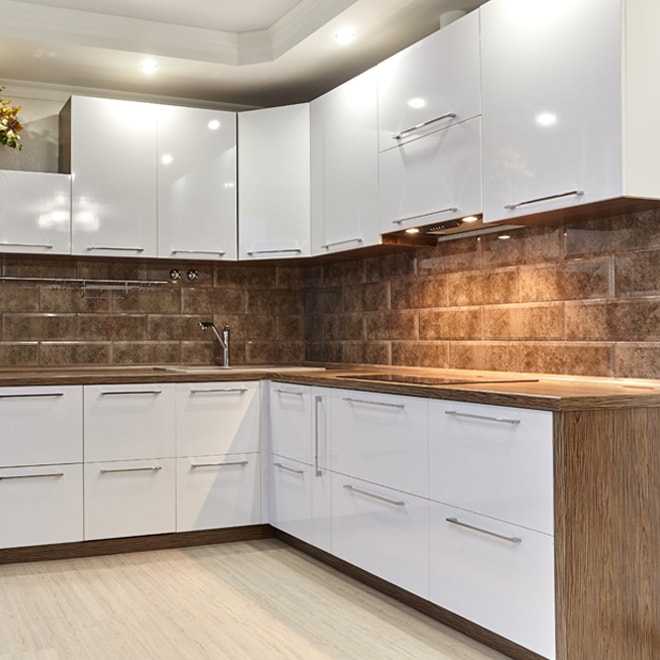

PVC (thermoplastic or thermofoil)
Made from fibreboard covered with a PVC sheet.
Advantages
- More durable than laminate or melamine
- Low maintenance
- Mouldable to any shape
Disadvantages
- More expensive than laminate
- Limited range of colours and finishes
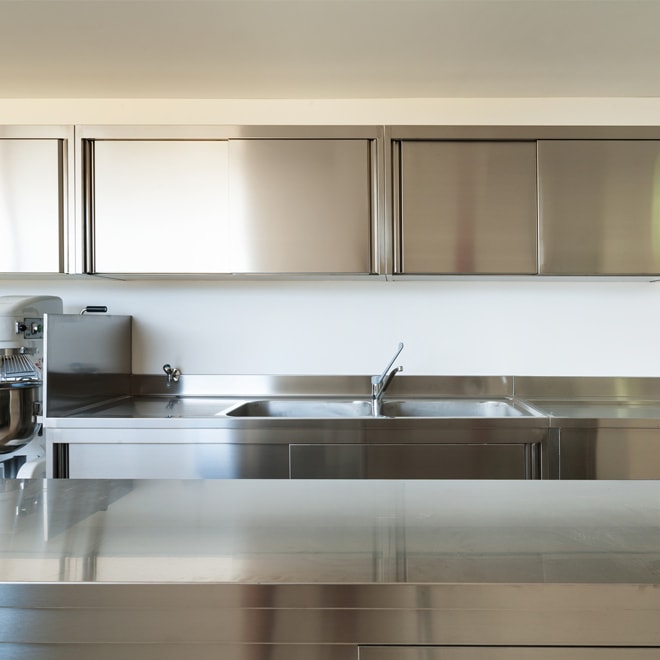

Stainless steel
Stainless steel cabinets look good in modern decors.
Advantages
- Resistant to humidity and temperature changes
- Eco-friendly
Disadvantages
- Shows scratches and fingerprints
- Requires frequent cleaning
- Costly
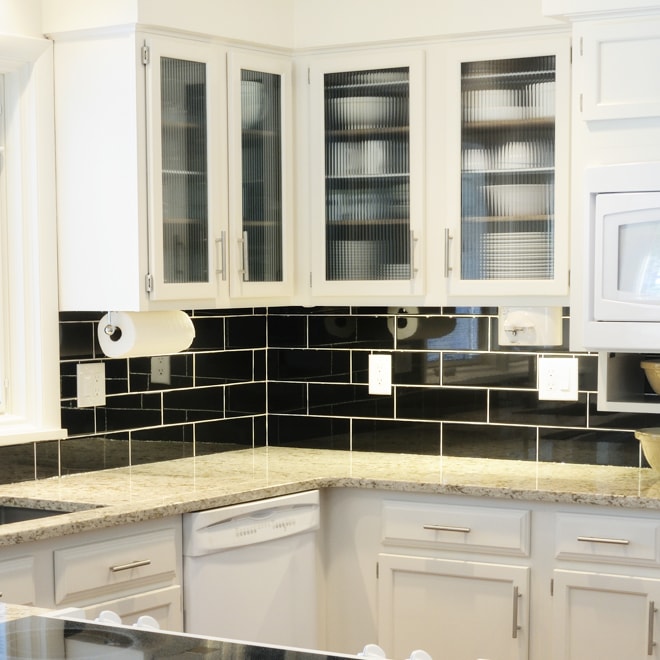

Glass
Clear, textured or frosted, glass lets the light through and brightens the room.
Advantages
- Makes room look larger
- Ideal for displaying decorative items
- Extensive choice of finishes
Disadvantages
- Shows fingerprints and clutter
- Fragile
You may also like
42 Pine Base Kitchen Cabinets With Drawers
Source: https://www.rona.ca/en/workshop/guides/choosing-kitchen-cabinets